BOUTIQUEResouces
Cell transfection plays a crucial role in scientific research, yet it is also one of the most easily overlooked steps. The level of transfection efficiency not only affects experimental results but may even render the obtained results invalid. In cell transfection experiments involving various types of nucleic acids, researchers often need to further optimize transfection conditions to achieve optimal efficiency—this is especially true for hard-to-transfect cells. However, selecting specialized transfection reagents tailored to specific cell types is only the first step toward the success of transfection experiments.
Founded in 1995, Mirus Bio has focused on and specialized in the field of nucleic acid delivery for many years. Its product lineup ranges from the early TransIT®-LT1 (known for low toxicity) to the GMP-grade TransIT-VirusGEN® (suitable for AAV and LV production; see Figure 1 for the product annual catalog). As of the publication of this manuscript, more than 10,000 articles have been published using Mirus products, and these published articles, together with Mirus’ database, cover over 1,200 cell types.
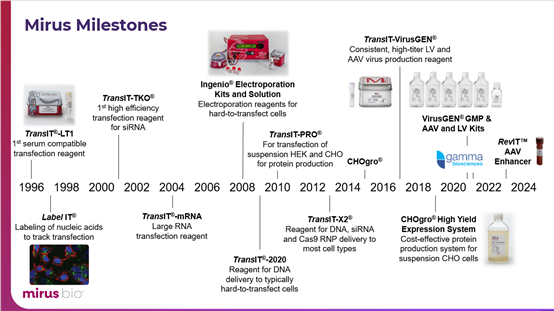
Figure 1 Mirus Product Annual Catalog
In cell transfection experiments, researchers often overlook the evaluation of transfection efficiency/success rate. So, are there corresponding technologies or methods that allow real-time monitoring of the successful delivery of DNA/RNA and their distribution status within cells? The Mirus Bio Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit provides a solution for researchers. The Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit enables efficient and direct labeling of any type of nucleic acid, with a one-step experimental procedure. Based on a non-enzymatic labeling method, it covalently attaches the selected label (fluorescence, biotin, digoxigenin, etc.) to the nucleic acid without damaging the integrity of the nucleic acid or affecting gene expression.
The Label IT® Kit offers a variety of labels to choose from, including Cy®3, Cy®5, CX-Rhodamine, TM-Rhodamine, Fluorescein, MFP488, Digoxigenin, Biotin, and Dinitrophenyl (DNP). The Label IT® Nucleic Acid Modification Kit (Amine) can also be used for DNA or RNA modification based on amine functional groups. The product features are as follows:
· Applicable for labeling any DNA or RNA template – suitable for multiple applications (In vitro & In vivo), such as CRISPR gene editing, nucleic acid delivery, RNA interference/expression experiments, FISH, Microarray, etc.;
· One-step labeling – simple and easy to complete a stable template labeling reaction;
· Adjustable labeling density according to experimental needs or applications – to achieve optimal sensitivity for detecting labeled DNA or RNA;
· Based on covalent chemical reaction – the modification of nucleic acid residues is permanent and non-damaging, making it an ideal choice for a variety of scientific research applications.
What is nucleic acid labeling? How to label nucleic acids? How to detect (them)?
The vast majority of molecular and biology-based in vitro and in vivo studies rely on the labeling or tagging of nucleic acids. Ideally, such labels or tags should not affect nucleic acid functions or research results. Therefore, a variety of nucleic acid labeling methods have been developed, which can be roughly classified into the following two categories:
· Chemical labeling method: It is based on reactive groups that bind to nucleic acids. For example, the Mirus Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit falls into this category, and the entire reaction process does not require the involvement of enzymes.
The Label IT® chemical labeling reagent consists of three components (see Figure 2):
(1) Label/Tag (green area);
(2) Linker, which interacts electrostatically with nucleic acids (yellow area);
(3) Alkylating group in the Label IT® reagent that covalently binds to active heteroatoms in nucleic acids (blue area).
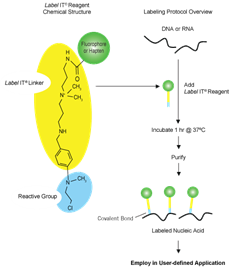
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram of Label IT® Labeling Molecule
Enzymatic reaction-based labeling method: Through enzymatic reactions, labeled and modified nucleic acids are added during the reaction process.
Once the nucleic acid to be studied is labeled, detection can be performed in the following two ways:
· Direct detection: In this case, the labeled nucleic acid contains a reporter molecule that can be used for optical, luminescent, or fluorescent signal generation.
· Indirect detection: The labeled nucleic acid carries a tag or label, which needs to specifically bind to a reporter-conjugated molecule. For example, biotin binds to fluorescently labeled streptavidin, and digoxigenin binds to fluorescently labeled specific antibodies, etc.
Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit — Does Not Alter Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
Research on gene silencing-related functions plays an important role in molecular and cellular biology, and chemical transfection also plays a crucial part in this research field. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are often used as the type of nucleic acid for studying protein functions in various cell types; they affect gene expression through effective knockdown. Then, will the addition of Label IT®-labeled nucleic acids alter the nucleic acid structure, thereby affecting subsequent experimental results?
For the evaluation test, the Label IT® siRNA Tracker? Kit was used. The same siRNA was added with different labels (Cy?3, Cy?5, Fluorescein, CX-Rhodamine) and without a label. After transfection, the labeled siRNAs could be observed via fluorescence microscopy. The gene expression results showed that the target gene expression levels of siRNAs with different labels were similar, which means that the addition of Label IT®-labeled nucleic acids does not affect the expression and function of the target gene (Figure 3).
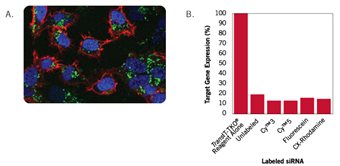
Figure 3 Evaluation Test of the Label IT® siRNA Tracker? Kit
-
Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit — Examples of Cutting-Edge Applications
Application 1: Enrichment of CRISPR'd Cells Using Label IT® Technology
In their article, Nasri, Mir, and colleagues described how to enrich cells successfully edited by CRISPR/Cas using Label IT® technology. One of the biggest challenges in genome editing experiments is successfully screening/enriching successfully edited cells from unedited ones—this becomes even more difficult when unedited cells have a growth/proliferation advantage over successfully edited cells.
To efficiently distinguish between gene-edited and unedited cells, the authors fluorescently labeled the CRISPR guide RNA (gRNA) using Label IT® before the gRNA formed a complex with Cas9 and was transfected into cells. The schematic diagram of the experimental workflow is as follows:
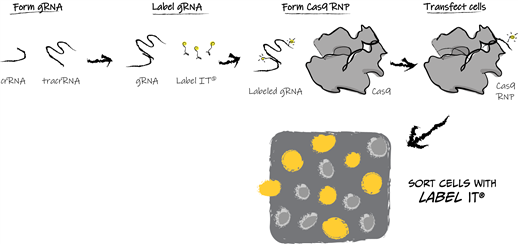
The research results showed that the gRNA labeled with Label IT® did not affect gene editing efficiency, and the successfully edited cell populations could be sorted/enriched via fluorescence. Furthermore, the researchers applied this CRISPR experimental workflow to GADD45B gene editing experiments targeting a variety of cell types. Depending on the cell type, the proportion of successfully edited cells in the Label IT®-labeled cell subpopulation was 15-40% higher than that in the total cell population.
Publication Information
Title: Fluorescent labeling of CRISPR/Cas9 RNP for gene knockout in HSPCs and iPSCs reveals an essential role for GADD45b in stress response
Author: Masoud Nasri, Perihan Mir et al.
Magazine: Blood Adv, Volume 3(1), Jan 2019.
DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017015511
Application 2: Focusing on Immune System Research Using Label IT® Technology
Label IT® nucleic acid labeling technology can be used in the characterization research of a new type of vaccine injection method—microneedle array (MNA). The traditional vaccine injection method involves subcutaneous injection with a needle longer than 3 centimeters, while the microneedle array is composed of micron-scale needles (schematic diagram shown below). It penetrates the skin subtly in a painless manner, reaching areas rich in immune cell populations, which can reduce patients' discomfort.
To enhance the efficacy of vaccines, immune-stimulatory molecules or "agonists" are typically incorporated into vaccine formulations alongside the vaccine's target or antigen. Research by Edwards et al. has shown that double-stranded polyIC RNA and single-stranded CpG DNA oligonucleotides can serve as agonists in microneedle arrays (MNAs). Furthermore, the researchers proposed that electrostatic interactions between negatively charged nucleic acid agonists and positively charged antigens facilitate the assembly of microneedle arrays. By using Label IT® Cy®3 and Cy®5 to fluorescently label these two types of nucleic acids respectively, the distribution of the labeled nucleic acids on the microneedles can be easily visualized. This enables researchers to uniformly incorporate the two agonists into the microneedle arrays at the specific required ratio, thereby making it possible to precisely modulate the immune response of MNA-based vaccines.
Publication Information
Title: Tuning innate immune function using microneedles containing multiple classes of toll-like receptor agonists
Author: Camilla Edwards, Robert Oakes et al.
Magazine: Nanoscale, Volume 15, Apr 2023.
DOI: 10.1039/D3NR00333G
Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit - Product Selection
There are four forms of the Label IT® Kit available to meet the needs of researchers for different application scenarios in nucleic acid labeling experiments:
· Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits
· Label IT®Tracker? Intracellular Nucleic Acid Localization Kits
· Label IT® siRNA Tracker? Intracellular Localization Kits
· Label IT® Nucleic Acid Modifying Kits
The table below summarizes the differences between different types of Label IT® Kits:
|
|
Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling |
Label IT® Tracker? |
Label IT® siRNA Tracker? |
Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Modifying |
|
Application |
Labeling of Various Types of Nucleic Acids for In Vitro & In Vivo Applications |
In Vitro & In Vivo Plasmid Tracking Experiments |
In Vitro & In Vivo siRNA Tracking Experiments |
Amino Modification of DNA |
|
Kit Components
|
Label IT® Reagent Reconstitution Solution
10X Labeling Buffer
Reagent D1& Buffer N1
G50 Microspin Columns |
Label IT® Reagent Reconstitution Solution
10X Labeling Buffer |
Label IT® Reagent Reconstitution Solution
10X Labeling Buffer
siRNA Dilution Buffer |
Label IT® Reagent Reconstitution Solution
10X Labeling Buffer
Reagent D1& Buffer N1
G50 Microspin Columns |
|
Label IT®: Nucleic Acid Ratio |
1 μl : 1 μg |
0.5 μl : 1 μg |
1 μl : 1 μg |
0.5 μl : 1 μg |
|
Labeling Density |
One label per 20-60 bp |
每60-140 bp 1個標記 |
每15-40 bp 1個標記 |
每20-60 bp 1個標記 |
|
Type of Label / Label Type |
· Cy®3
· Cy®5
· Fluorescein
· CX-Rhodamine
· TM-Rhodamine
· Biotin
· MFP488
· Digoxigenin
· DNP
|
· Cy®3
· Cy®5
· Fluorescein
· CX-Rhodamine
· TM-Rhodamine
· Biotin
|
· Cy®3
· Cy®5
· Fluorescein
· CX-Rhodamine
· TM-Rhodamine
· Biotin
|
Amino group |
|
Kit Specifications
|
25 μl
100 μl |
50 μl |
50 μl |
25 μl
100 μl |
For more frequently asked questions (FAQ) about the product, please refer to the official website link.
Label IT® Nucleic Acid Labeling Kit - Optimization of Nucleic Acid Labeling Density in Experiments
The ideal density depends on the type of nucleic acid to be labeled and the downstream application. In experiments that require direct tracking of nucleic acids, a higher nucleic acid labeling density is more suitable; whereas in experiments aiming to maintain or fully preserve the biological functions of labeled nucleic acids, a lower labeling density is more appropriate. With the Label IT® nucleic acid labeling technology, it is easy to adjust to the ideal labeling density.
The change in the ratio (v:w) of Label IT® reagent to nucleic acid shows a linear correlation with the labeling density (Figure 4). For example, according to the recommended initial experimental protocol, 5 μl of Label IT® reagent should be added to label 5 μg of DNA, resulting in a v:w ratio of 1:1. Under the condition that the incubation time and the amount of DNA remain unchanged, if the amount of Label IT® reagent is reduced to 2.5 μl or increased to 10 μl, the labeling density will be halved or doubled, respectively.
Experimental Tip: Using an excessively high amount of Label IT® reagent (more than 4 times the recommended amount) may lead to nucleic acid cleavage or quenching of the fluorescent groups in Label IT®.
The nucleic acid labeling density has a positive linear correlation with the amount of Label IT® reagent used and the incubation time of the reaction. The desired ideal labeling density can be easily and flexibly adjusted by modifying the amount of Label IT® reagent in the reaction or the reaction incubation time (the incubation temperature remains at 37°C).
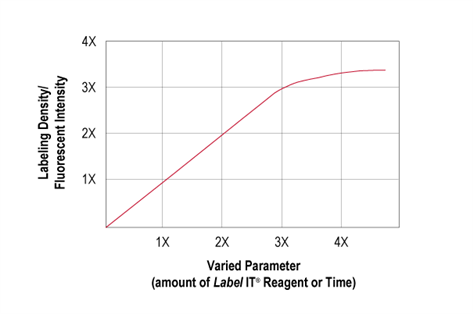
Figure 4. Nucleic acid labeling density is proportional to the amount of Label IT® reagent and reaction incubation time
Experimental Tip: For instructions on how to calculate nucleic acid labeling density, including detailed experimental procedures and methods, please refer to "Calculate Nucleic Acid Labeling Density".
Introduction to Mirus Bio
Founded in 1995, Mirus has always been committed to providing optimized methods and efficient tools for gene delivery. With over 25 years of in-depth exploration and dedication in the transfection field, the company has achieved multiple technological breakthroughs and has become a global leader and trusted brand in the nucleic acid delivery industry. The team of scientists at Mirus continuously pushes the boundaries of transfection technology and has launched the VirusGEN® Transfection Reagent and RevIT? Enhancer. These products further increase AAV/Lv yields, help promote cost reduction and efficiency improvement in biotherapeutic drugs, and empower customers in the cell and gene therapy (CGT) field.

Beijing XMJ Technology Co., Ltd. is the general agent of Mirus in China. Adhering to a professional and rigorous attitude, we have been providing customers with high-quality products and services. Mirus' best-selling transfection products are always available in stock. If you are interested in the above-mentioned products, please feel free to send email to info@xmjsci.com or visit the website www.gq44.cn to learn more product information.


 京公網(wǎng)安備 11010802028692號
京公網(wǎng)安備 11010802028692號