BOUTIQUEResouces
In recent years, the biopharmaceutical industry has shown a trend of prosperous development. A large number of macromolecular biologics have been approved for marketing by regulatory authorities, and many other innovative macromolecules are in the late clinical stage or pre-marketing application stage, which will soon bring benefits to patients. For example, monoclonal antibodies expressed based on CHO cells, recombinant proteins or nanobodies expressed based on E. coli systems, adeno-associated viruses (AAV) expressed based on HEK293 cells or insect cell line SF9, and virus-like particles (VLP) expressed based on yeast cells. Different from traditional small-molecule chemical drugs, the expression systems of biological macromolecules are more complex, with more types of impurities (such as residual host cell proteins (HCP) and residual host cell DNA (HCD)), and the impurity structures are relatively complex. These factors pose great challenges to downstream purification.
Chromatographic processes based on traditional microsphere technology are important means for the purification of biological macromolecules, which have advantages such as stable process performance and good scalability. In recent years, multimodal chromatography resins have attracted increasing attention. Multimodal chromatography resins usually have at least two interaction mechanisms, among which the most common one is the combination of ion exchange mode and hydrophobic interaction mode, which can effectively purify target molecules over a wide range of pH and conductivity.
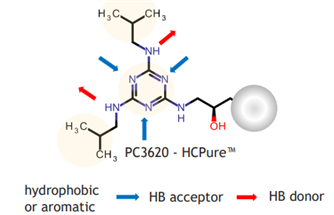
Figure 1. Ligand Structure and Mode of Action of HCPure?
HCPure? is a multimodal chromatography resin launched by Astrea Bioseparations (UK) in 2023. The resin matrix is composed of highly cross-linked agarose with a uniform particle size, and the matrix is modified with chemically synthesized small-molecule ligands (Figure 1). It mainly binds impurities in the feed solution through hydrophobic interactions, while also exhibiting hydrogen bonding interaction mode—this differs from the mechanism of action of mainstream commercially available products and thus forms a complementary solution. Suitable for a variety of expression systems, HCPure? can robustly remove process-related or product-related impurities such as host cell proteins (HCP), host cell DNA (HCD), aggregates, and molecular fragments from the feed solution under a wide range of loading conditions. Table 1 shows the impurity removal capacity of HCPure? in common expression systems.
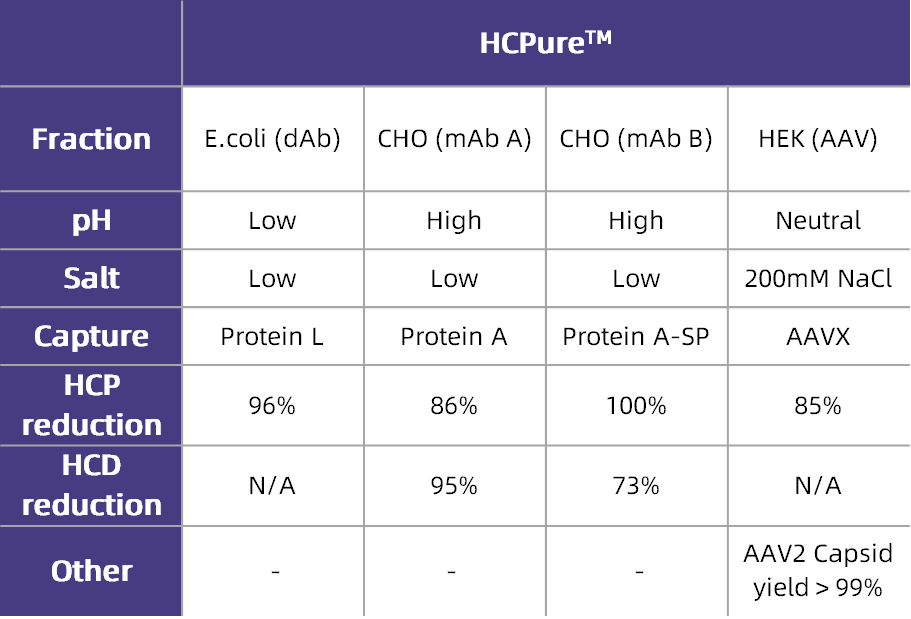
Table 1. Application Effects of HCPure? in Various Expression Systems
1. HCPure? Enables Effective HCP Removal in E. coli Expression Systems
In this application case, researchers used E. coli to express the nanobody Vκ. The harvest was first purified via Protein L affinity chromatography. After neutralization, the eluate was adjusted to different pH values (6.0–8.0) and conductivities (6–18 mS/cm). Subsequently, the sample was loaded onto HCPure? in flow-through mode. The flow-through and wash fractions were collected, and the contents of Vκ and HCP were detected to explore the optimal loading conditions for HCPure?. The test conditions are shown in the table below:

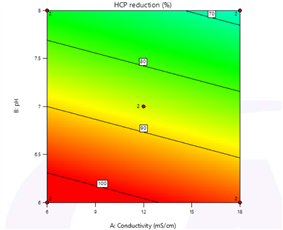
Figure 2. Investigation of Loading pH and Conductivity for HCPure? in E. coli Expression Systems
As can be seen from the test results in Figure 2, under the loading conditions of lower pH (6.0) and lower conductivity (6 mS/cm), the HCP removal effect is optimal, and the recovery rate of the target molecule Vκ is the highest. Under the optimal loading conditions, the HCP in the feed solution can be reduced from 30,000 ppm to 200 ppm (representing an HCP removal capacity of 2 log values), and the Vκ recovery rate exceeds 85% (Table 2).
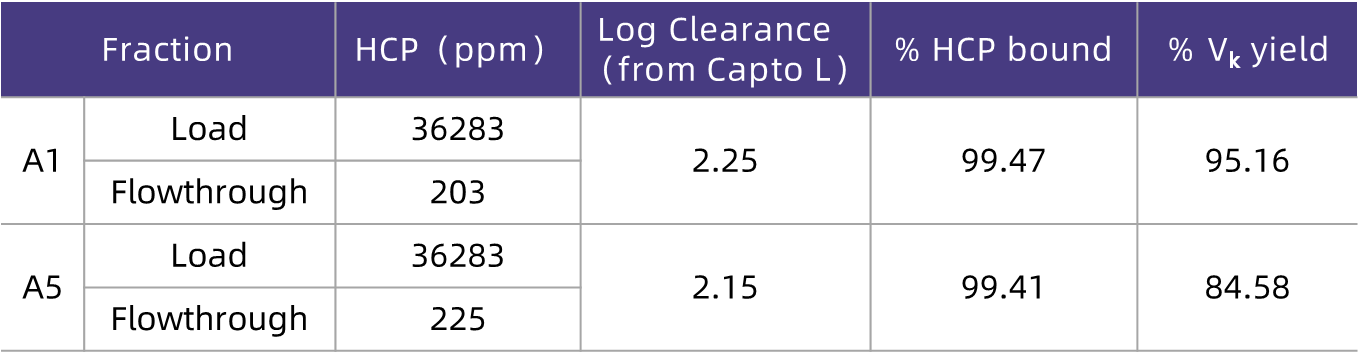
Table 2. Effective HCP Removal by HCPure? in E. coli Expression Systems
2. HCPure? Enables Effective HCP Removal in CHO Cell Expression Systems
In this application case, researchers used CHO cells to express IgG-type monoclonal antibodies. The clarified harvest was first purified via Protein A affinity chromatography. After neutralization, the eluate was adjusted to different pH values (4.0–9.0) and conductivities (8–18 mS/cm), and then loaded onto HCPure? in flow-through mode. The flow-through and wash fractions were collected, and the contents of IgG and HCP were detected. Among these conditions, the sample with pH 6.0 and conductivity 12 mS/cm was the neutralized eluate from affinity chromatography without additional adjustment.
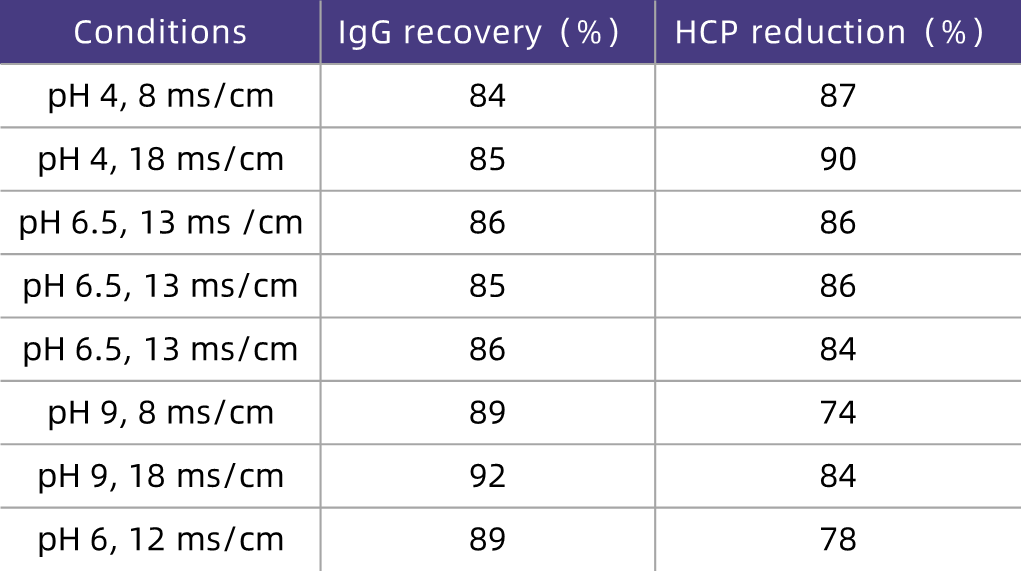
Table 3. Effective HCP Removal by HCPure? Under Different Loading pH and Conductivity Conditions in CHO Cell Systems
As can be seen from the test results in Table 3, HCPure? can effectively remove HCP from the loading feed solution (with an average removal rate of 84%) over a wide range of loading pH and conductivity, while maintaining a high recovery rate of the target molecule (with an average of 87%). In addition, since the condition of pH 6.0 and conductivity 12 mS/cm corresponds to the initial neutralized eluate from affinity chromatography, the feed solution can be directly loaded onto HCPure? after affinity chromatography without adjustment or buffer exchange. This not only maintains excellent recovery rate and HCP removal efficiency but also significantly saves process time and costs.
3. HCPure? Enables Effective Aggregate Removal in CHO Cell Expression Systems
In this application case, researchers used CHO cells to express IgG-type monoclonal antibodies. After the feed solution was purified via Protein A affinity chromatography and cation exchange chromatography, it was incubated under conditions of low pH and high conductivity to induce the formation of high levels of aggregates. Subsequently, the sample was loaded onto HCPure? in flow-through mode. The flow-through and wash fractions were collected, and the aggregate content was detected.
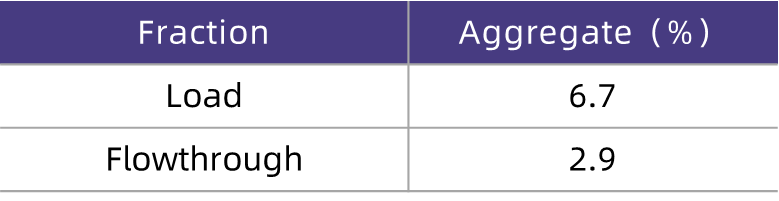
Table 4. HCPure? Enables Significant Removal of Aggregates from Antibody Feed Solutions
As can be seen from the test results (Table 4), after the feed solution was purified by HCPure?, the aggregate content decreased from the initial 6.7% to 2.9%, demonstrating that HCPure? can significantly remove aggregates from the feed solution.
4. HCPure? Enables Effective HCP Removal in HEK 293 Cell Expression Systems
In this application case, researchers used HEK 293 cells to express adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV-2) via transient transfection. After the viral vector was purified by affinity chromatography, it still contained a relatively high level of low-molecular-weight protein impurities. The affinity chromatography eluate was exchanged into PBS + 200 mM NaCl (pH 7.5) and then loaded onto HCPure? (a chromatography column with an inner diameter of 10 mm and a column height of 10 cm) in flow-through mode, with a total loading volume of 5.0E+13 VP. The flow-through and wash fractions were collected for analysis.

Figure 3. SDS-PAGE Detection Results
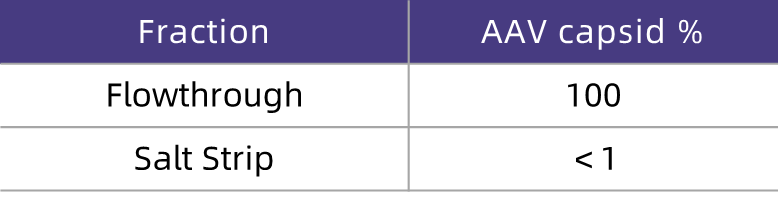
Table 5. ELISA Detection Results
As can be seen from the SDS-PAGE results (Figure 3), the flow-through fraction contains most of the viral capsid protein bands of VP1, VP2, and VP3 (Lanes 8–13), while the regeneration fraction (Lane 14) contains a large number of low-molecular-weight protein impurity bands. This indicates that HCPure? can effectively remove protein impurity molecules from the feed solution. According to the ELISA detection results (Table 5), almost all the viral capsid proteins in the flow-through fraction are recovered (nearly 100%), demonstrating that HCPure? can maintain excellent AAV recovery while removing protein impurities.
Properties of HCPure?
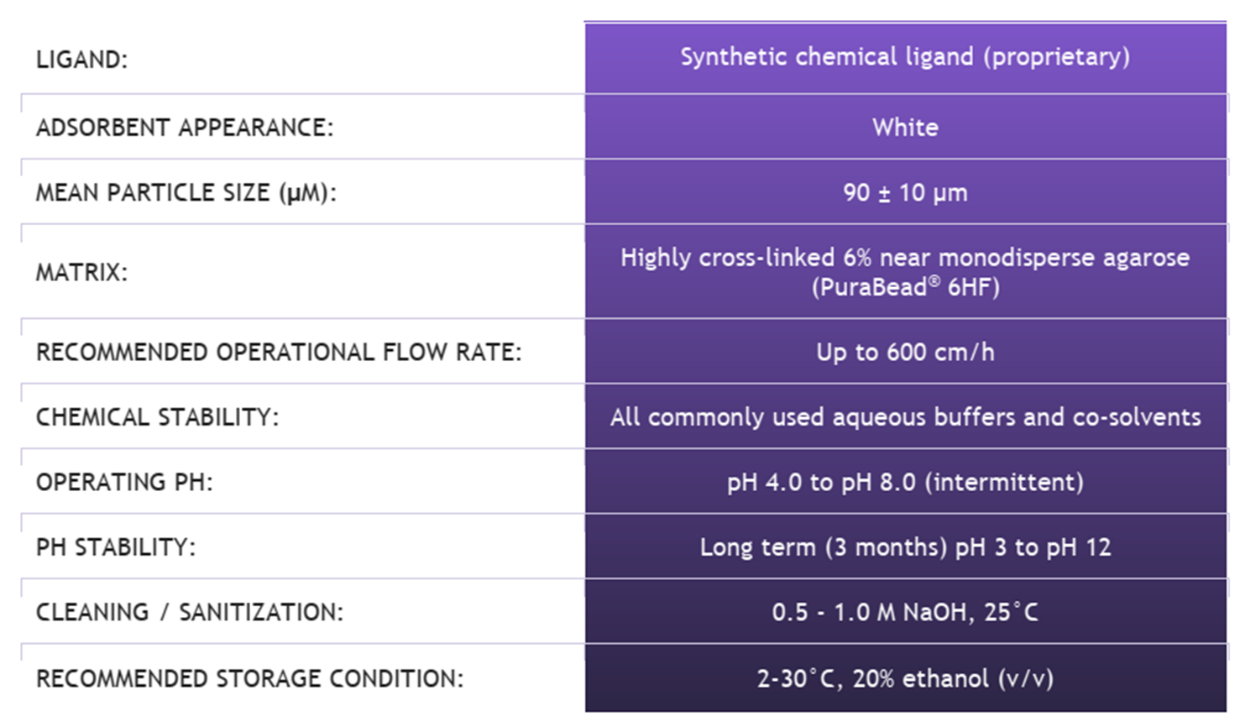
Product Information for HCPure?
Adsorbent Gel Slurry
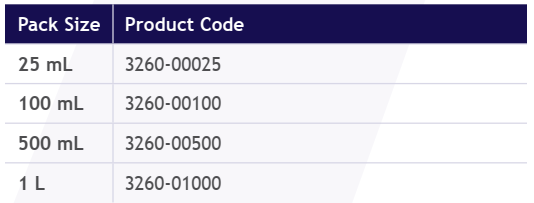

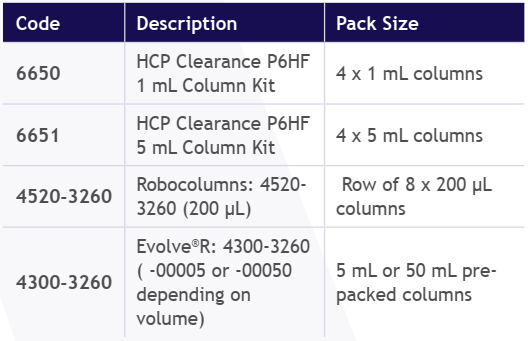
Pre-Packed Columns

If you are interested in the above products, please click here to fill in your information. Technical experts from Astrea Bioseparations will provide you with personalized optimization solutions to effectively help you solve difficult problems in your purification process.

Astrea Bioseparations was incubated at the University of Cambridge in 1987. With over 30 years of experience in the R&D and production of chromatographic media, it is a world-class supplier of chromatographic media products and services. To date, more than 21 manufacturing processes using Astrea's products have obtained approvals from the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency).
Astrea Bioseparations has 3 R&D and production bases worldwide, focusing on providing industry-leading chromatographic media and technical services for the fields of biological macromolecules and CGT (Cell and Gene Therapy). The novel nanofiber-based chromatographic technology launched by Astrea Bioseparations addresses the issues of low capacity and time-consuming processes associated with traditional bioseparation tools. It enables faster, more environmentally friendly, and more cost-effective purification processes,

XMJ is the authorized distributor of Astrea Bioseparations in China, providing users with comprehensive technical support and after-sales service. Please feel free to send email to info@xmjsci.com or visit the official website www.gq44.cn at any time for more information.
References
- J. Kreusser et al., Influence of pH value and salts on the adsorption of lysozyme in mixed-mode chromatography, 2021
- R. Hess et al., Standardized method for mechanistic modeling of multimodal anion exchange chromatography in flow through operation, 2023
- Technical Note: HCPURE?: A FIT FOR PURPOSE HOST CELL PROTEIN CLEARANCE SOLUTION IN E. COLI WORKFLOWS, Astrea Bioseparations
- Technical Note: HCPure? host cell protein clearance resin: Mixed mode chromatography as a means of process intensification, Astrea Bioseparations
- Technical Note: HCPure? host cell protein clearance resin: Mixed mode chromatography as a means of process intensification, Astrea Bioseparations
- Technical Note: HCPURE?: HOST CELL IMPURITY REMOVAL IN CHO WORKFLOWS, Astrea Bioseparations
- Technical User Guide: HCPureTM, Astrea Bioseparations


 京公網(wǎng)安備 11010802028692號
京公網(wǎng)安備 11010802028692號