BOUTIQUEResouces
Introduction
Host Cell Protein (HCP) ELISA detection methods must undergo method validation in accordance with regulatory-approved experimental protocols (such as ICH or FDA guidelines) to ensure they produce accurate results. Essentially, obtaining accurate HCP ELISA results requires two key conditions: the HCP concentration in the sample must be above the kit’s Limit of Quantitation (LOQ), and the detection antibodies for HCP must be in excess. To meet these two conditions, dilution linearity validation of test samples (process samples and final drug substance bulk) is imperative. Therefore, dilution linearity is one of the critical experiments for verifying the specificity and accuracy of HCP ELISA methods.
There are two main reasons for poor dilution linearity in HCP detection:
1. The excess antibody condition is not satisfied for certain HCPs in the sample, requiring further dilution to reach the "Minimum Required Dilution" (MRD);
2. The product protein itself or certain components in the product formulation buffer interfere with HCP detection. In such cases, samples can be treated using designated sample diluents (see end of article) or buffer exchange to meet detection requirements.
Regarding sample diluents, the optimal choice is to use the same diluent as that for the standard. Cygnus provides corresponding sample diluents for each ELISA detection method to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of test results. For users of Cygnus HCP ELISA kits, we recommend defining acceptable dilution linearity as: "When performing two-fold dilutions, the corrected HCP concentration does not vary by more than ±20%". Additionally, detection values should be avoided from being close to the LOQ—specifically, the HCP detection value of the diluted sample must not be lower than twice the LOQ.
In the following sections, this article will provide a detailed explanation of the operating procedures and precautions for dilution linearity in HCP ELISA method validation.
Why Establish Dilution Linearity?
When testing a new HCP ELISA method, establishing dilution linearity is the first fundamental experiment. Its purpose is to confirm whether the selected HCP ELISA is suitable for detecting HCPs in your process samples and drug substance bulk. Once dilution linearity is confirmed, it provides the experimental condition information required for further analytical validation—hence, dilution linearity is typically the first validation experiment to be conducted.
Specifically, the objective of the dilution linearity experiment is to determine the reaction curve and full quantitation range of the ELISA method for HCPs in the sample. Successful validation of dilution linearity indicates that:
· The excess antibody condition is satisfied for all types of HCPs present in the sample;
· The sample matrix does not interfere with HCP quantitation.
Together, these ensure the reliability of HCP ELISA detection results.
How to Perform a Dilution Linearity Experiment?
Prior to ELISA analysis, any sample that may exceed the Upper Limit of Quantitation (ULOQ) should first undergo a dilution linearity experiment. The process involves the following steps:
1. Perform multiple gradient dilutions of the HCP test sample using a validated sample diluent;
2. Detect these diluted samples;
3. Calculate the corrected HCP concentration for each diluted sample (i.e., measured HCP concentration × dilution factor).
In most cases, after reaching a certain dilution factor, the corrected HCP concentration of the diluted sample will stabilize at a relatively constant value. This dilution factor is referred to as the "Minimum Required Dilution" (MRD).
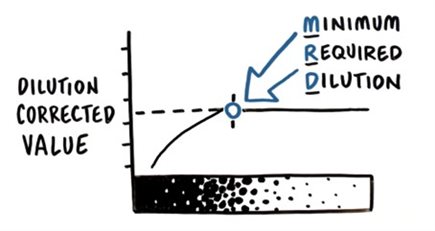
Figure 1. Minimum Required Dilution (MRD)
As shown in the example in the table below, the sample did not exhibit good dilution linearity at high concentrations (undiluted, 1:2 dilution, and 1:4 dilution). However, with further dilution, we can determine a Minimum Required Dilution (MRD)—the dilution factor at which acceptable dilution linearity is achieved (see the blue row in the table below). By definition, acceptable dilution linearity is achieved when the change in corrected HCP concentration between two-fold dilutions does not exceed ±20%. Meanwhile, detection values should be kept away from the Limit of Quantitation (LOQ); specifically, the HCP detection value of the diluted sample must not be lower than twice the LOQ (in this example, the HCP detection value of the 1:64 diluted sample was < 2×LOQ, so it was excluded from the statistics).
The percentage change is calculated by subtracting the corrected concentration of the previous diluted sample from that of the current one, then dividing the difference by the corrected concentration of the previous diluted sample. For instance, the percentage change of the 1:2 diluted sample relative to the undiluted sample is calculated as follows: [(233 - 146)/146] × 100% = 60%.
|
Sample Dilution Gradient |
HCP Dilution-Corrected Value (ng/mL) |
Percentage Change from the Previous Diluted Sample |
|
Undiluted |
146 |
NA |
|
1:2 |
233 |
60% |
|
1:4 |
312 |
34% |
|
1:8 |
361 |
16% |
|
1:16 |
356 |
1% |
|
1:32 |
370 |
4% |
|
1:64 |
未計算
(<2倍LOQ) |
NA |
From the data in the table, we can conclude that the Minimum Required Dilution (MRD) for this sample is 1:4. Therefore, the final calculated HCP concentration should be the average of all dilution-corrected HCP concentrations that fall at or below the MRD and above the Limit of Quantitation (LOQ). (In this example, the average of 312, 361, 356, and 370—i.e., 350 ng/mL—should be used.)
In practical applications, we should evaluate the dilution linearity for all sample types requiring HCP detection (including process samples and the final drug substance bulk). Additionally, the MRD values for each sample type and matrix, as well as specific guidelines for diluting different samples, should be incorporated into Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) documents.
Causes of Poor Dilution Linearity and Corresponding Solutions
In HCP ELISA detection, poor dilution linearity may occur for certain HCPs, which means the "excess antibody condition" is not satisfied for those specific HCPs in the sample. For instance, individual HCPs at high concentrations may saturate the antibodies targeting them, leading to the "high-dose hook effect"—a phenomenon that results in inaccurate quantitation of the affected HCPs.
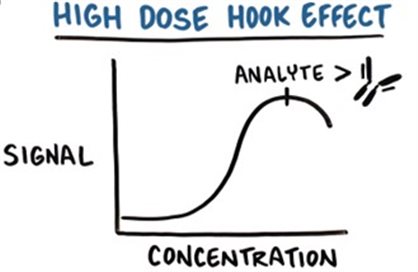
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram of the High-Dose Hook Effect
Additionally, certain hitchhiker proteins may interact with product proteins and become significantly enriched during the purification process, thereby completely interfering with the linearity of the entire assay.
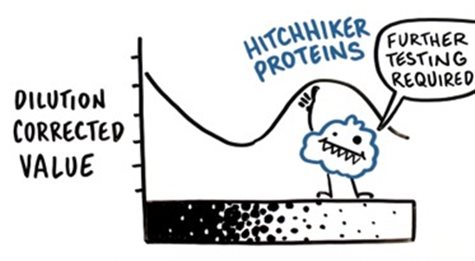
Figure 3. Hitchhiker Proteins Interfering with Assay Linearity via Interaction with
Other factors that may also lead to poor dilution linearity include interference with the detection process by certain components in the product formulation (or the buffer solution of process samples). For Cygnus HCP ELISA kits, known interfering factors include extreme pH, detergents, organic solvents, high protein concentrations, and high salt concentrations. Therefore, we recommend that samples must be diluted using the same diluent as that for the standards, as detailed in the table below.
Item No.
Product Name
Application
Specification
I028
Sample Diluent
Suitable for Most HCP Kits, such as CHO(F550-1),E.coli(F1020, F410)etc.
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
I700
Sample Diluent
Suitable for HEK 293 HCP (F650S) Kit
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
I094
Sample Diluent
Suitable for MDCK (F800) and HeLa (F810) HCP Kits
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
I600
Sample Diluent
Suitable for Most Kits in the Mix-N-Go Series, Including Protein A Detection Kits (F600, F610, F740, F910, F950, etc.) and Restriction Endonuclease Residue Detection Kit (F960)
25 ml, 100 ml
F031A
Sample Diluent
Suitable for BSA (F030) Detection Kit
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
I800
Sample Diluent
Suitable for PROchievA? Protein A (F965) Kit
25 ml, 100 ml
F223A
Sample Diluent
Suitable for NS/0 HCP (F220) Kit
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
F233A
Sample Diluent
Suitable for A549 HCP (F230) Kit
100 ml, 500 ml
F213A
Sample Diluent
Suitable for Goat IgG (F210) Detection Kit
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
F243A
Sample Diluent
Suitable for Goat Milk Total Protein (F230) Detection Kit
100 ml, 500 ml, 1000 ml
Overview of Sample Diluents for Cygnus Bioprocess Impurity Detection Kits (by Kit Type)
Finally, we emphasize again that the dose-response curve will exhibit a positive slope and the detection results will be accurate only when antibodies are in excess.
If poor dilution linearity is caused by insufficient HCP antibodies or sample matrix interference, the measured HCP concentration will show an upward trend as the sample dilution factor increases. Therefore, it is necessary to further dilute the sample to achieve the Minimum Required Dilution (MRD). For other causes, the accuracy of detection can also be improved by optimizing experimental procedures. If increasing the sample dilution factor still fails to resolve the issue of poor dilution linearity, there may be a problem with the purification process.
Cygnus provides a corresponding Qualification Summary (QS) document for each type of detection kit. If needed, please click here to fill in the information to request it, or contact Ximeijie (the exclusive distributor of Cygnus in China). If you encounter dilution linearity-related issues when using Cygnus HCP ELISA kits and cannot resolve them through the aforementioned methods, you are also welcome to contact Ximeijie at any time—our technical support team will provide corresponding solutions and suggestions for your specific problems. In the future, we will continue to share a series of content on HCP ELISA method validation, including spike recovery and HCP antibody suitability validation.

For over 25 years, Cygnus Technologies has specialized in providing products and analytical methods for the biotechnology and biopharmaceutical industries, with the aim of accelerating the research and development (R&D) phase and enhancing product quality. Cygnus develops and manufactures bioprocess residue detection kits, which are used to detect specific impurities across more than 50 different expression systems. As an expert in high-sensitivity analytical technologies focused on immunoassays for biotechnological applications, Cygnus’ products and services are utilized by over 95% of biopharmaceutical companies worldwide and have gained broad recognition from regulatory authorities such as the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), NMPA (National Medical Products)
![]()
As the exclusive distributor of Cygnus in China, Beijing XMJ Technology Co., Ltd. has established long-term and stable cooperative relationships with numerous well-known domestic pharmaceutical companies and CRO/CMO enterprises. Over the years, Ximeijie’s products and services have helped many enterprises accelerate the R&D phase, enhance drug quality, purity and safety, optimize R&D processes more efficiently, shorten time-to-market for products, and reduce QC costs. If you are interested in the aforementioned products, please feel free to send email to info@xmjsci.com or visit the website www.gq44.cn for more information.


 京公網(wǎng)安備 11010802028692號
京公網(wǎng)安備 11010802028692號